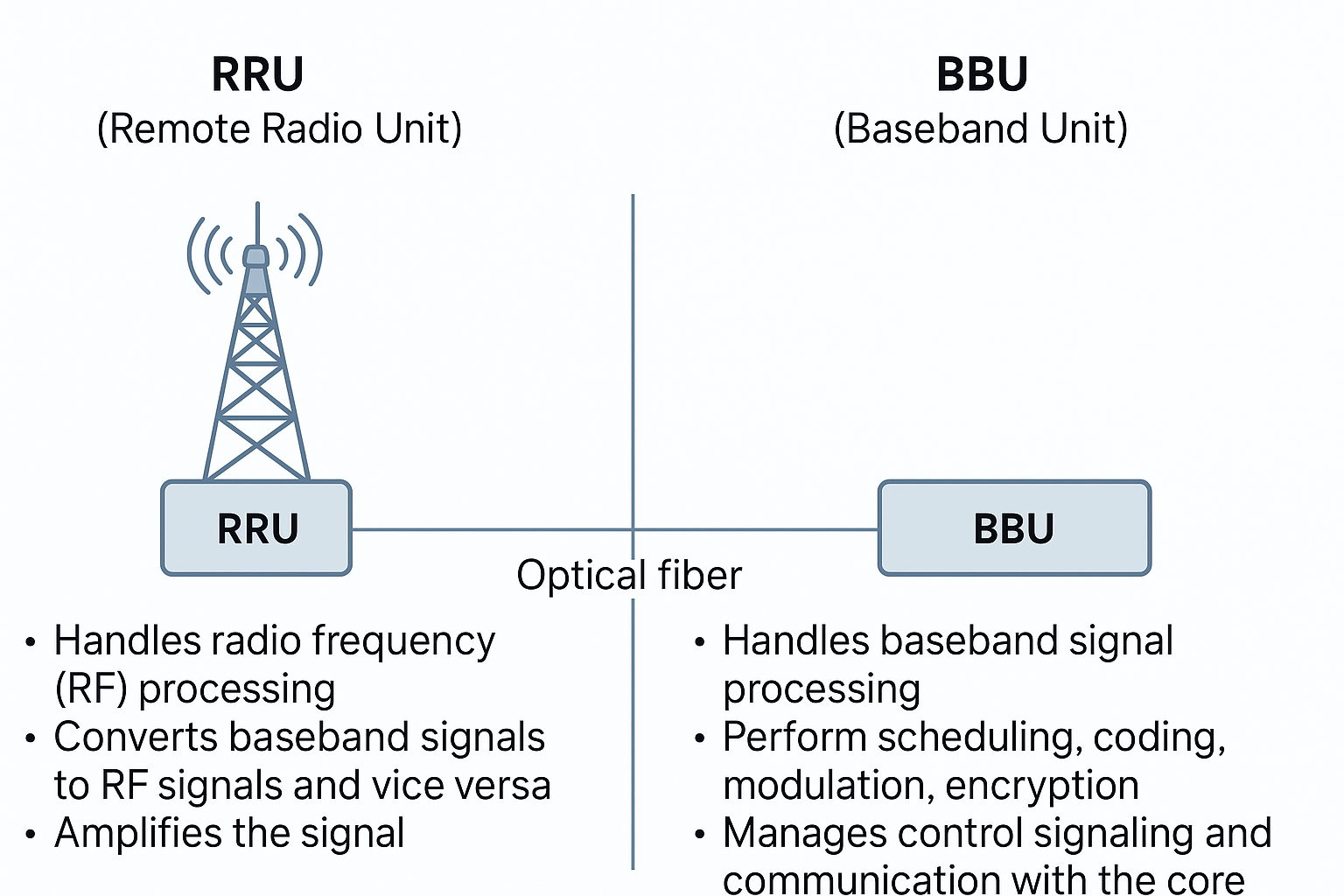
In telecom networks — especially in 4G LTE and 5G — the RRU (Remote Radio Unit) and BBU (Baseband Unit) are two key components of a base station, but they serve very different purposes. Here’s a clear breakdown:
📡 RRU (Remote Radio Unit)
Also called: RRH (Remote Radio Head)
Function:
- Handles radio frequency (RF) processing — the part that sends and receives radio signals to/from user devices (phones, modems, etc.).
- Converts baseband signals from the BBU into RF signals and vice versa.
- Amplifies the signal before sending it through the antenna.
Location:
- Installed near or integrated with the antennas (usually on a tower, rooftop, or pole).
- Close to the antenna to reduce signal loss over cables.
Main tasks:
- RF amplification and filtering
- Analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion
- Power amplification
- Transmission over the air interface (Uu interface in LTE)
🧠 BBU (Baseband Unit)
Function:
- Handles baseband signal processing — all the digital signal processing and protocol stack functions.
- Performs scheduling, coding, modulation, encryption, and resource management.
- Manages control signaling, handovers, and communication with the core network.
Location:
- Usually installed at the base of the cell tower or in a centralized location (in newer architectures like C-RAN).
Main tasks:
- Baseband processing (modulation/demodulation, encoding/decoding)
- Radio resource control (RRC)
- Communication with the core network (EPC/5GC) via the S1 interface
- Management of multiple RRUs in some setups
🧩 Connection between RRU and BBU
- The RRU and BBU are connected by optical fiber using the CPRI (Common Public Radio Interface) or eCPRI protocol.
- This connection transmits digitized radio signals and control data between them.
⚙️ In short:
| Component | Full Name | Location | Main Role | Handles |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RRU | Remote Radio Unit | Near antenna | Radio frequency processing | RF transmission & reception |
| BBU | Baseband Unit | Ground or centralized site | Digital signal & control processing | Baseband, protocols, scheduling |
🧠 Analogy:
Think of it like a human body:
- The BBU is the brain – it decides what to do, processes information, and manages coordination.
- The RRU is the mouth and ears – it actually transmits and receives signals.
Would you like me to include how this architecture evolves in 5G (with CU/DU/RU split) too? It’s a natural next step after understanding BBU/RRU.