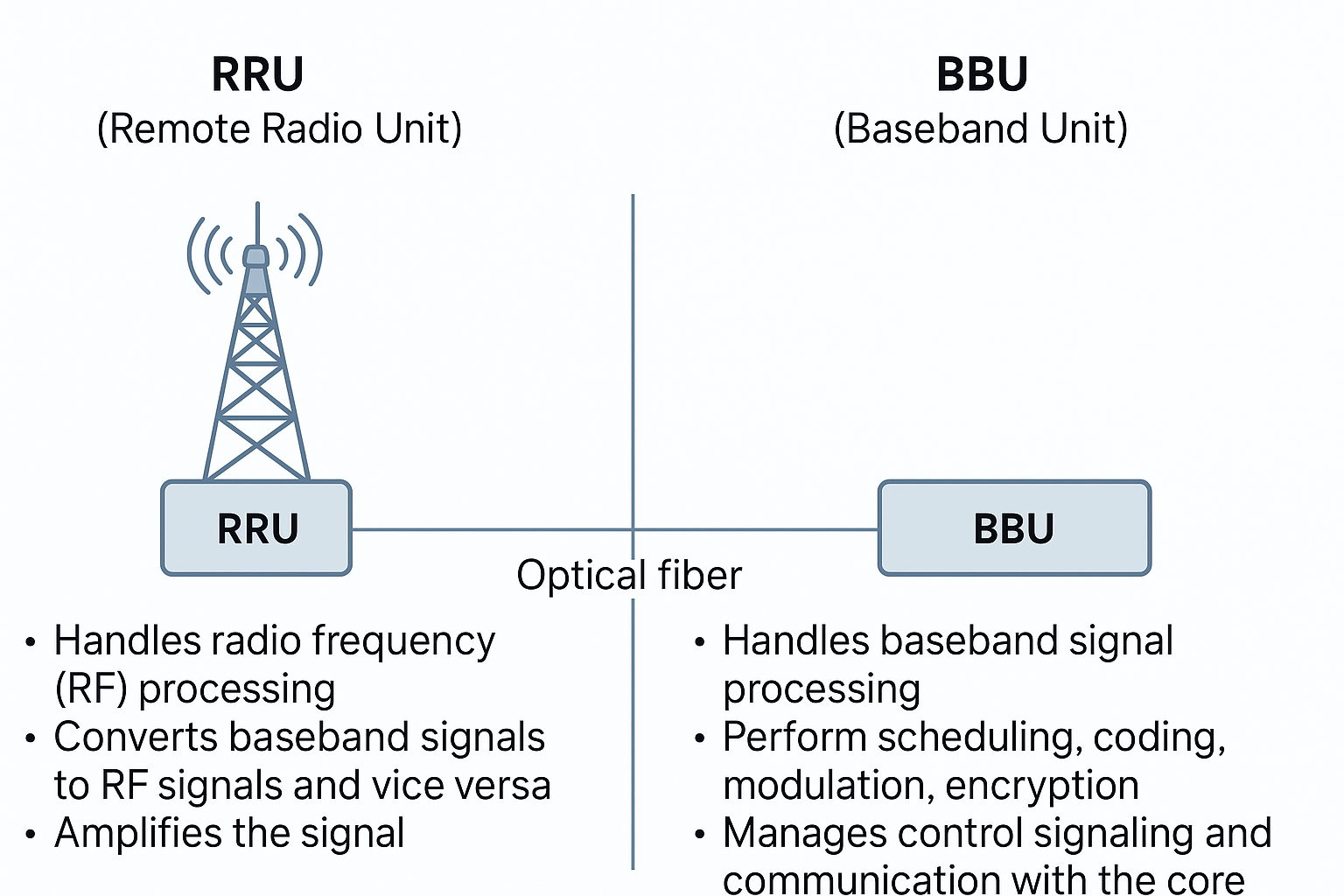
In a 5G (Fifth Generation) wireless network, the Radio Remote Unit (RRU) plays a critical role in enabling high-speed, low-latency, and reliable wireless communication. Its elementary role and functionalities in a 5G network include:
- Signal Transmission and Reception:
- The fundamental function of an RRU in 5G is to transmit and receive radio signals. It serves as the bridge between user devices (such as smartphones or IoT devices) and the core network.
- RRUs receive data from the central baseband unit (BBU) and convert it into radio signals for transmission to user devices.
- They also receive incoming radio signals from user devices, digitize them, and send the data to the BBU for further processing.
- Beamforming and Massive MIMO:
- 5G networks heavily rely on beamforming and Massive Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output (MIMO) technology to enhance data rates and network capacity. RRUs are equipped with multiple antennas and can dynamically adjust the phase and amplitude of transmitted signals to form narrow beams directed towards specific user devices, improving signal quality and capacity.
- RRUs in 5G networks also support Massive MIMO, which involves using a large number of antenna elements to serve multiple users simultaneously, increasing spectral efficiency.
- Frequency Bands and Bandwidths:
- RRUs in 5G are designed to support a wide range of frequency bands and bandwidths to accommodate different spectrum allocations and deployment scenarios. This flexibility allows operators to allocate the right resources for different use cases, including enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC), and massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC).
- Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS):
- 5G RRUs support Dynamic Spectrum Sharing, which enables the simultaneous operation of 4G LTE and 5G NR (New Radio) on the same frequency band. This feature helps in a smooth transition from 4G to 5G and maximizes spectrum utilization.
- Synchronization and Timing:
- In 5G networks, precise synchronization is essential, especially for features like ultra-low latency and network slicing. RRUs maintain strict synchronization with the network’s timing references to ensure seamless coordination between cells and optimal network performance.
- Energy Efficiency:
- RRUs in 5G networks are designed with energy efficiency in mind. They can adjust their power output based on network demand, traffic load, and environmental conditions, helping reduce energy consumption and operational costs.
- Remote Management and Monitoring:
- RRUs are often deployed at cell sites, including macrocells and small cells. They include remote management and monitoring capabilities that allow network operators to configure, update, and troubleshoot these units remotely, reducing the need for on-site visits.
- Latency Reduction:
- RRUs contribute to the overall reduction of network latency in 5G by processing and transmitting data more efficiently, enabling applications that require ultra-low latency, such as autonomous vehicles and augmented reality.
In summary, the elementary role of RRUs in a 5G network is to handle the radio transmission and reception, implement advanced technologies like beamforming and Massive MIMO, support flexible frequency bands, and contribute to the overall performance, efficiency, and reliability of the 5G network. They are essential components that enable the realization of the full potential of 5G technology and its diverse range of use cases.