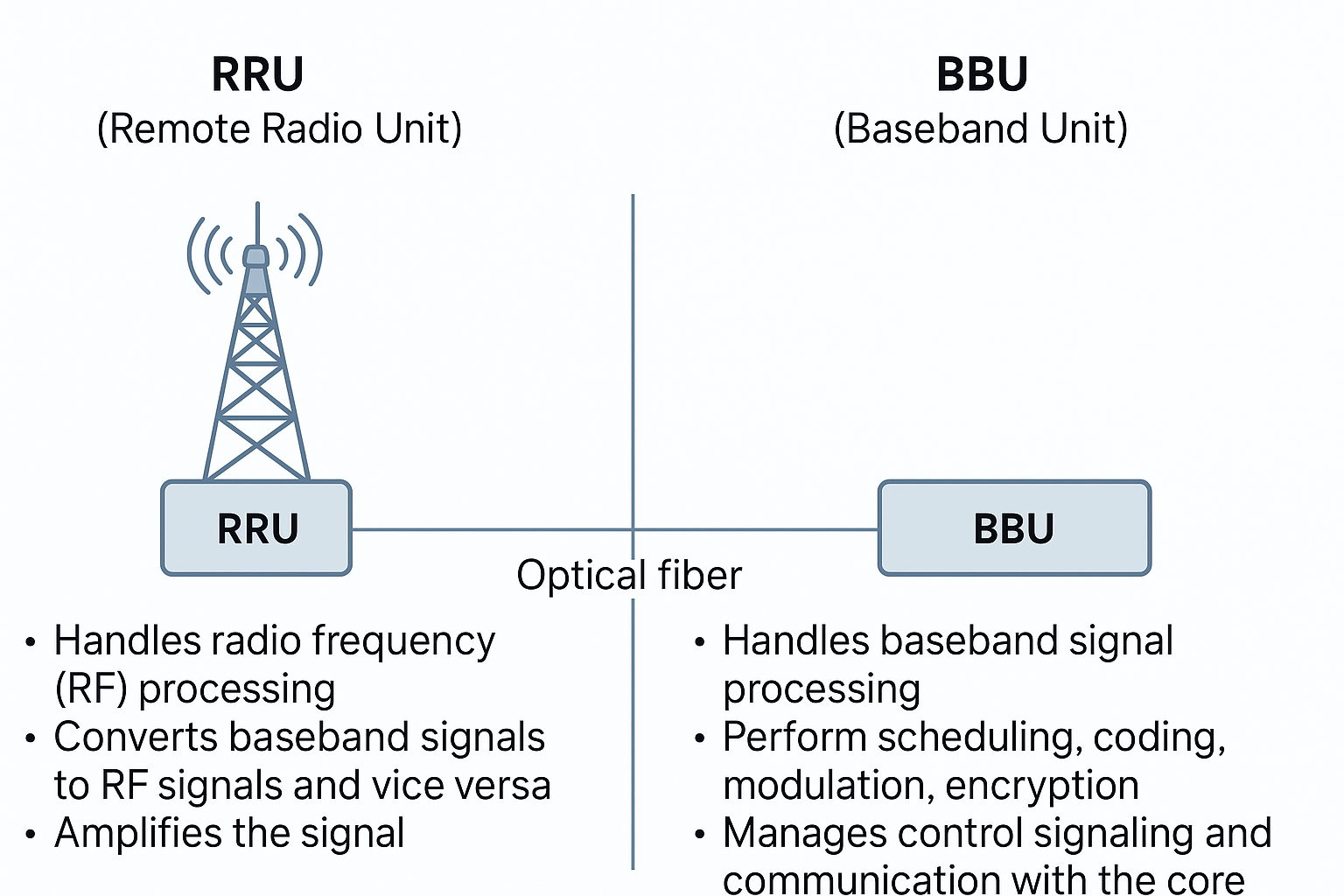
🧠 BBU (Baseband Unit)
Function:
The BBU handles the digital processing part of the base station. It’s like the „brain“ of the radio site.
Responsibilities:
- Signal modulation/demodulation
- Coding/decoding
- Call setup and management
- Communication with the mobile core network
- Resource management and control functions
Location:
Often located at a central site or near the cell tower base.
📡 RRU (Remote Radio Unit)
Function:
The RRU handles the radio frequency (RF) part — transmitting and receiving signals over the air.
Responsibilities:
- Converts baseband signals to RF and vice versa
- Amplifies the signal for transmission
- Filters and processes the incoming signal
- Interfaces directly with the antenna
Location:
Usually mounted near the top of the tower or on rooftops — close to the antenna to reduce signal loss.
🔌 How They Work Together
Think of it like this:
- The BBU does all the digital processing and decision-making.
- The RRU acts like the hands and ears, transmitting and receiving the actual wireless signal.
- They are connected by fiber optic cable (usually via CPRI or eCPRI).
✅ Summary Table
| Component | RRU (Remote Radio Unit) | BBU (Baseband Unit) |
|---|---|---|
| Role | RF signal transmission & reception | Baseband signal processing |
| Location | On tower/antenna (outdoor) | On ground/in shelter (indoor) |
| Interfaces with | Antenna and BBU | RRU and core network |
| Processing type | Analog + some digital | Fully digital |
In New Architectures (like 5G C-RAN):
- Multiple RRUs connect to one centralized BBU pool.
- This makes the network more flexible, easier to manage, and cheaper to scale.
Let me know if you want a diagram to visualize this or a comparison with newer units like DU and RU in 5G.