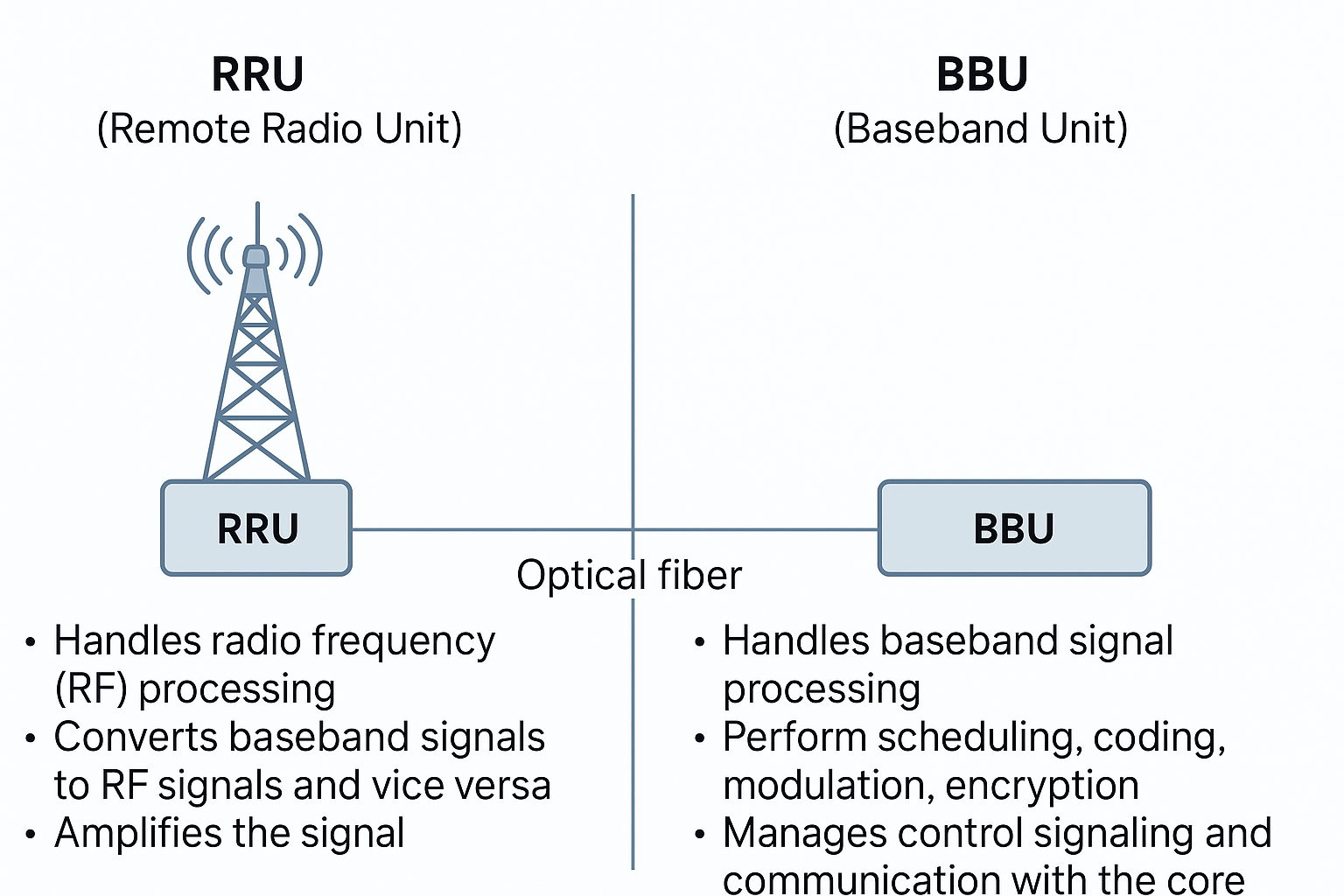
The BBU (Baseband Unit) is a crucial component in a 5G (Fifth Generation) network, responsible for several critical functions that contribute to the network’s overall operation and efficiency. Its role in the 5G network call flow includes the following functionalities:
- Digital Signal Processing:
- The BBU is responsible for processing digital data. It takes in data from various sources, including upper-layer protocols and user devices, and performs functions like encoding, decoding, modulation, demodulation, error correction, and signal shaping.
- Radio Resource Management:
- BBU plays a significant role in managing radio resources efficiently. It determines how to allocate resources like time, frequency, and power to various user devices and services based on network conditions, traffic load, and quality of service requirements.
- Scheduling and QoS Management:
- BBU is responsible for scheduling transmissions to and from user devices. It determines which users get access to the network resources at a given time, taking into account factors such as priority, service type (e.g., voice, video, data), and quality of service (QoS) requirements.
- Modulation and Coding:
- BBU selects the appropriate modulation and coding schemes for data transmission based on the channel conditions and the device’s capabilities. It aims to maximize data rates while maintaining reliable communication.
- Signal Combining and Splitting:
- In scenarios where multiple antennas are used (e.g., Massive MIMO), the BBU combines signals from multiple RRUs (Radio Remote Units) for transmission and splits incoming signals from multiple antennas to process them separately for reception.
- Beamforming Control:
- BBU is responsible for controlling beamforming in the network. It determines the beamforming weights and phase adjustments for each RRU in a coordinated manner to steer beams towards user devices for better signal quality and coverage.
- Interference Management:
- The BBU monitors and manages interference in the network. It employs techniques like interference cancellation and coordination between cells to minimize interference and maximize the network’s spectral efficiency.
- Latency Control:
- BBU plays a role in minimizing latency in the network. It ensures that data processing and transmission are performed as efficiently as possible to meet the low-latency requirements of 5G services, including applications like autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
5G Network Call Flow Involving BBU:
- When a user initiates a call or data session, the BBU is involved in several stages of the call flow.
- It receives requests from user devices through the RRU and processes these requests.
- BBU selects the appropriate modulation and coding schemes, assigns resources, and schedules the transmission.
- During the call or data session, the BBU continues to monitor network conditions and adjust resource allocation and beamforming as needed to maintain high-quality communication.
- When the call or data session ends, the BBU releases allocated resources and ensures proper handover or session termination.
Overall, the BBU in a 5G network is responsible for managing the core baseband processing tasks and coordinating the communication between user devices and the radio access network (RAN), including the RRUs. It plays a central role in ensuring the efficient operation of the network and the delivery of high-speed, low-latency, and reliable wireless services.